- 021-91034194
- Info@pishco.ir
- Tehran, Sa'adat Abad
Home » What is biogas, how is it produced, and what are its uses?
Biogas is a natural and renewable energy source that plays an important role in the environment and industry. This gas is produced by the decomposition of organic materials such as manure, food waste and sewage. The biogas production process is carried out through anaerobic digestion (without the presence of oxygen). Methane, which makes up between 50 and 70 percent of the biogas composition, turns it into a flammable gas. The combination of gases such as methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide with oxygen – which comprises about 21 percent of ambient air – produces fuel and releases energy.
Biogas is one of the most cost-effective types of renewable fuels that has been exploited in many countries. This energy source is used for applications such as cooking, heating and cooling, electricity generation, methanol and steam production, efficient waste disposal, and mechanical power supply.
In the 10th century BC in Assyria and in the 16th century in Iran, biogas was used to heat water for bathing and washing the body. In 1776, Alexander Volta concluded that there was a direct relationship between the amount of decaying organic matter and the volume of flammable gas.
In 1859, the first anaerobic fermentation system was built in Bombay, India. Also in 1860, the first unit used to treat wastewater solids was set up by a man named H. Moore S.
Some of the most widely used biomass sources include crop residues, municipal and industrial wastewater, agricultural materials, animal manures, seaweed, food processing wastes, and paper waste; however, the range of feedstocks that can be used in this field is much wider.
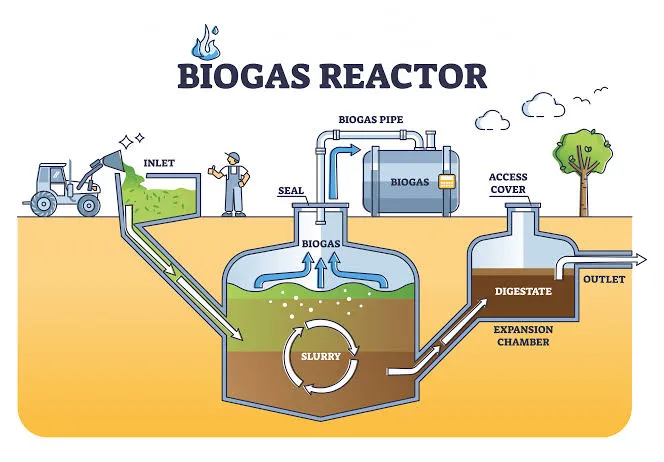
The digester is an air- and moisture-proof chamber with a special inlet for biomass injection. The raw materials to be converted into energy are first pre-processed and then placed inside this chamber. After that, agitators periodically move the biomass to release gases.
Biogas can be obtained by processing various types of organic waste. As a renewable energy source, this gas is completely environmentally friendly. The use of biogas is used in various fields, including fueling road vehicles. The production of this gas also plays an effective role in improving the economic situation, as the need to import fossil fuels is reduced, preventing the outflow of foreign exchange. If you are interested in taking advantage of biogas-related services, visit its dedicated page on our website.
Biogas can be produced from a variety of raw materials, but microorganisms that feed on biomass play a key role in the process. These microbes produce methane gas during anaerobic digestion. The process also produces organic nutrients that are useful for green farming.
The process of converting biomass into biogas is usually followed in four main steps:
Primary shredding: In the first step, the bio-waste is broken down into smaller pieces to facilitate digestion. To prepare the slurry, a liquid is added to the material to create a more suitable mixture for digestion.
Heating for microbial activity: In this step, the prepared mixture is heated to a temperature of about 37 degrees Celsius to provide favorable conditions for the activity of microorganisms.
Main digestion process: The main reactions of biogas production occur in large tanks and take about three weeks.
Final purification stage: Finally, the obtained gas is cleaned of impurities and carbon dioxide to prepare it for final use.
Finally, the produced biogas is transported to the place of consumption in liquid or gas form, depending on the need.
The biogas production process begins with the entry of raw materials into a dedicated plant. Suitable raw materials for biogas production include the following:
Industrial waste that is harmful to the environment, such as excess lactose
Spoiled food from stores and restaurants
All bio-waste
Sludge left over from treatment plants
Fertilizers and various biomasses
These materials are usually transported to the biogas plant pits by trucks or special waste transporters. After unloading, the waste is crushed and ground into a uniform form. Then, a nutrient liquid, such as water, is added to it to reduce the concentration of solid matter and create a more efficient process.
As it enters the tanks, some non-biodegradable waste is separated and sent to another facility for conversion into electricity or heat. The biomass that has passed the slurry stage is combined with similar materials and pumped into pre-digestion tanks, where enzymes produced by bacteria break down these compounds into usable molecules.
The next step is the disinfection of the biomass. In this step, all pathogens are destroyed by applying a temperature of over 70 degrees Celsius for one hour. The disinfected material is then transferred to the main reactor, where biogas is produced. Disinfection allows the use of these materials in agriculture, which we will discuss in detail in the following articles on green agriculture.
There are various ways to utilize biogas, including:
Exploitation for heat or steam production
Simultaneous generation of electricity and heat or mechanical power
Use as an energy source in industries to create heat, steam, electricity, or cooling
Use in chemical compound production processes
Consumption as fuel in vehicles
Transport through fuel pipeline networks
These applications have made biogas one of the most versatile and cost-effective energy sources in the world.
Recommended article: What is a Global Trade Item Identifier or GTIN code?
Biogas has many advantages compared to other fuel sources. The following are some of its most prominent uses and benefits:
Providing energy in the form of heat, light, and electricity
Significant reduction in the amount of waste thrown away
Contain and reduce disease-causing agents such as flies and parasite eggs
Converting organic waste into rich, high-quality fertilizer
Helping to preserve natural resources such as vegetation, soil, and water resources
Improving productivity in the livestock and agricultural sectors
These characteristics have made biogas a sustainable and environmentally friendly option.

Reducing pollution of water and soil resources
One of the significant benefits of biogas is its role in reducing pollutants in soil and water resources. Landfills often leak toxic substances into groundwater, while the anaerobic digestion process prevents the transmission of infectious diseases through water by destroying parasites.
Organic Fertilizer Production
By-products from the biogas process can be a good alternative to chemical fertilizers. These types of fertilizers are effective in enhancing plant growth, while the chemical compounds found in unnatural fertilizers sometimes lead to food poisoning.
Low cost of biogas production
The biogas production process is not only simple, but also economically viable. Setting up a small biogas production unit requires limited investment and can be used to provide the gas needed for cooking or electricity generation by using household waste or animal manure. Of course, on a larger scale, biogas is used more in industries, especially the automotive industry, in which case its cost-effectiveness decreases.
Reducing dependence on fossil fuels
Another important achievement of biogas production is the reduction of the need for fossil energy resources. Some countries, including China and India, have made extensive investments in this area. In particular, China has been able to significantly reduce the consumption of fuels such as coal, natural gas and oil by developing biogas power plants.
Better and healthier cooking
Using biogas in cooking produces much less pollution than other fuels. This gas produces heat quickly and saves cooking time. Also, burners that work with biogas often have the ability to adjust the flame to different degrees, which makes controlling the heat much easier.
Environmentally friendly
Biogas has a positive impact on nature by reducing greenhouse gases. Biogas power plants prevent methane from being released into the atmosphere by capturing it. Plants also help reduce pollutants by absorbing this gas and converting it into energy. Another notable point is that biogas does not require high energy consumption for production, and its raw materials, such as food waste, fertilizer, and waste, are renewable and always available resources.
Suggested article: What is green fuel and how is it produced?
A biogas plant is a facility that provides an oxygen-free environment for the anaerobic digestion process to take place. In simple terms, this engineered system allows waste to be converted into renewable energy and useful fertilizers with minimal negative impact on the environment.
A biogas plant consists of three basic parts, each of which plays an important role in gas production:
Initial preparation of materials
Biomass fermentation
Gas separation and storage
Since each type of biomass has its own unique characteristics, the fermentation process will be different in each case. As a result, the time required to produce biogas also varies based on the type of raw material used. For this reason, the use of a pretreatment stage in industrial biogas plants is common and effective.
Biofuel cells have great potential to power implantable medical devices, such as glucose biosensors. The technology could help remove organic compounds from waste streams without significant costs. There is also the potential to use these fuels to provide heating for buildings, commonly known as “bioheat.”
The biomass conversion process in the biogas reactor begins with the activity of microorganisms, and organic materials gradually enter the fermentation stage.
In fact, what happens in this section is that microbes utilize organic compounds such as carbohydrates, proteins and other biological components and, by decomposing these materials, transform them into methane and carbon dioxide. A large part of these compounds are converted into biogas within about three weeks. The gas produced is also collected and stored from the upper part of the reactor in a special spherical tank.
لطفا فرم زیر را به دقت پر کنید تا مشاورین ما در اسرع وقت با شما تماس حاصل فرمایند.
Please fill out the form below carefully so that our consultants will contact you as soon as possible.